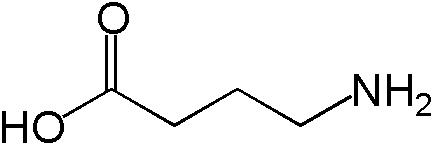
GABA(γ-アミノ酪酸)
γ-アミノ酪酸 gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) は抑制性の神経伝達物質です。
GABAB 受容体はGタンパク質共役受容体で、カリウムチャネルを開き、カルシウムチャネルを閉じることで神経伝達物質の放出を妨げます。
The G proteins phosphorylate serine/threonine residues, whereas YPK (tyrosine protein kinase) coupled G protein phosphorylates tyrosine, as the name applies. The YPK receptor has two types: one that phosphorylate serine/threonine which is mediated by second messenger, and one that directly phosphorylates tyrosine. The receptor site is extracellular, the kinase is in cytosol. The YPK which binds to EGF (epidermal), FGF (fibroblast), NGF (nerve), and insulin has one transmembrane and phosphorylates tyrosine.
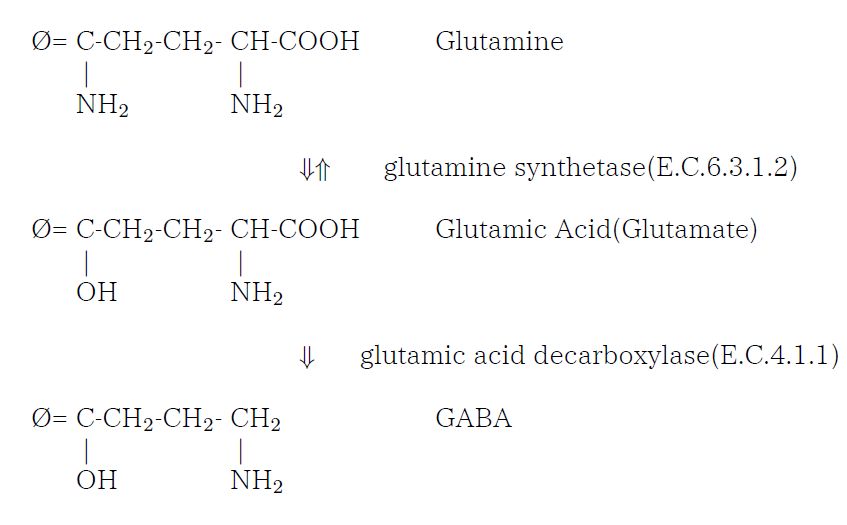
GABA の生成
γ-aminobutyricacid is synthesized from glutamine by GAD(glutamic acid
decarboxylase(E.C.4)). Glutamine is the most abundant protein in brain.
GABA pathway is inhibitory.
GABA の機能
抑制性の神経伝達物質であるGABA のアゴニストは鎮静作用がありますが、特定個所のニューロンの活動を抑制することで活動を活発化する働きがあります。
睡眠中のアセチルコリン性のニューロンの活動を抑制することで、REM睡眠が妨げられ、睡眠時間が長くなります[*]。
Marks, G. A., et al. “Blockade of GABA, Type A, Receptors in the Rat Pontine Reticular Formation Induces Rapid Eye Movement Sleep That Is Dependent upon the Cholinergic System.” Neuroscience, Elsevier Limited, 19 June 2015, utsouthwestern.influuent.utsystem.edu/en/publications/blockade-of-gaba-type-a-receptors-in-the-rat-pontine-reticular-fo.